哈喽,大家好,我是指北君。
相信大家日常开发中会经常写各种分支判断语句,比如 if-else ,当分支较多时,代码看着会比较臃肿,那么如何优化呢?
1、什么是策略模式?
Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
策略模式(Strategy Pattern):定义一族算法类,将每个算法分别封装起来,让它们可以互相替换。
2、策略模式定义
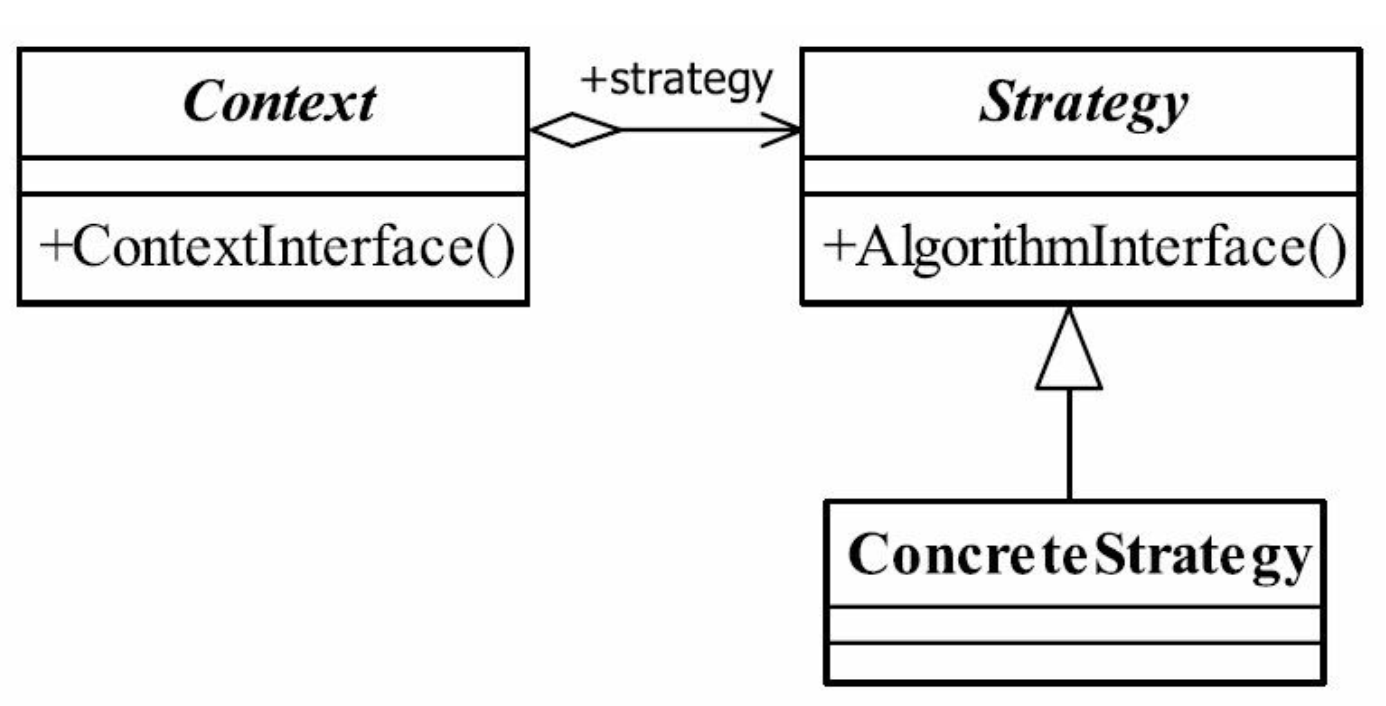
①、Context封装角色
它也叫做上下文角色, 起承上启下封装作用, 屏蔽高层模块对策略、 算法的直接访问,封装可能存在的变化。
②、Strategy 抽象策略角色
策略、 算法家族的抽象, 通常为接口, 定义每个策略或算法必须具有的方法和属性。
③、ConcreteStrategy 具体策略角色
实现抽象策略中的操作, 该类含有具体的算法。
3、策略模式通用代码
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
测试:
1 | |
4、用策略模式改写if-else
假设我们要处理一个office文件,分为三种类型 docx、xlsx、pptx,分别表示Word文件、Excel文件、PPT文件,根据文件后缀分别解析。
4.1 常规写法
1 | |
处理逻辑全部放在一个类中,会导致整个类特别庞大,假设我们要新增一种类型处理,比如对于2007版之前的office文件,后缀分别是 doc/xls/ppt,那我们得增加 else if 逻辑,违反了开闭原则,如何解决这种问题呢,答案就是通过策略模式。
4.2 策略模式改写
1 | |
1 | |
// 省略 OfficeHandlerXlsxStrategy/OfficeHandlerPptxStrategy 类
1 | |
测试:
1 | |
4、策略模式优点
①、算法可以自由切换
这是策略模式本身定义的, 只要实现抽象策略, 它就成为策略家族的一个成员, 通过封装角色对其进行封装, 保证对外提供“可自由切换”的策略。
②、避免使用多重条件判断
简化多重if-else,或多个switch-case分支。
③、扩展性良好
增加一个策略,只需要实现一个接口即可。
5、策略模式应用场景
①、多个类只有在算法或行为上稍有不同的场景。
②、算法需要自由切换的场景。
③、需要屏蔽算法规则的场景。
